The Bank Account feature in your ERP system provides a centralized location to manage all the bank accounts associated with your business. This feature helps ensure that your financial transactions are accurately recorded, and it enables seamless management of your banking details, whether for making payments, receiving funds, or reconciling accounts.
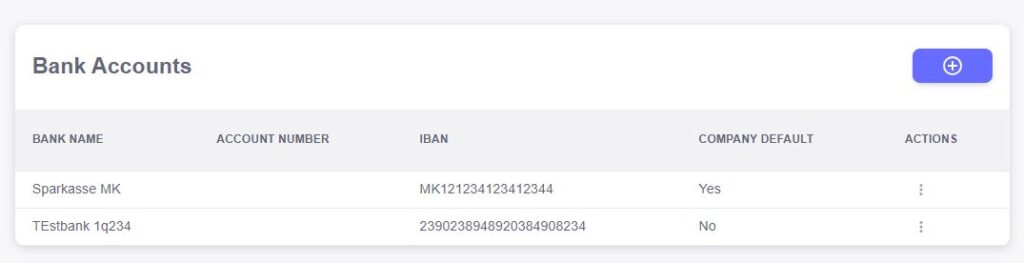
Bank Name
The “Bank Name” field allows you to specify the name of the bank where your account is held. This is an important field for identifying the financial institution associated with each account, ensuring you can easily manage and differentiate between multiple bank accounts within the system.Account Number
The “Account Number” field records the unique number associated with your business’s bank account. This is essential for making transfers, deposits, or withdrawals, and it helps ensure that all financial transactions are accurately directed to the correct account.IBAN
The “IBAN” (International Bank Account Number) field allows you to enter the internationally recognized account number for cross-border transactions. Providing your IBAN ensures that your business can receive international payments smoothly and meet global banking standards.Company Default
The “Company Default” field lets you mark a specific bank account as your default account for transactions. This ensures that the selected account is automatically used for payments, receipts, and other financial activities, making it easier to manage your finances without having to manually select the account each time.Actions
The “Actions” field provides quick access to essential functions related to each bank account, such as edit, delete, or view details. This feature ensures that you can easily update your bank account information, remove outdated accounts, or view important account details whenever necessary.
The Create Bank Account feature in your ERP system allows you to add new bank accounts to your system with ease. By providing essential banking details, you can ensure that your financial transactions are well-organized and that you have accurate, up-to-date information for managing payments, receipts, and reconciliations.
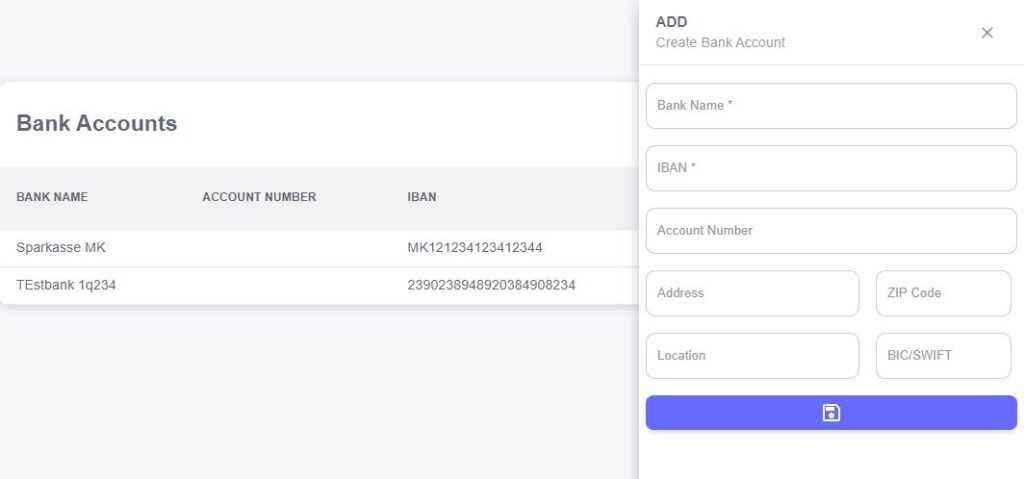
Bank Name
The “Bank Name” field allows you to enter the name of the financial institution where your bank account is held. Accurately recording the bank’s name ensures proper identification and helps differentiate between multiple bank accounts, especially when you’re working with different banks for various financial operations.IBAN
The “IBAN” (International Bank Account Number) field is used to enter your international bank account number. This is crucial for conducting cross-border transactions, as the IBAN provides a standardized way to identify bank accounts internationally. It ensures that payments are routed correctly, especially for overseas transfers.Account Number
The “Account Number” field captures your bank account’s unique number. This number is essential for making transfers, receiving payments, and accurately tracking your financial activity. Entering this number ensures that your bank account is linked correctly to your system.Address
The “Address” field allows you to enter the bank’s physical address. Including the full address of the bank is useful for maintaining a complete record of the bank’s details and may be necessary for certain banking or legal requirements.Zip Code
The “Zip Code” field captures the postal code of the bank’s location. This ensures that the address is fully documented and can be used for correspondence or verification purposes. The zip code also helps when working with multiple branches or locations of a bank.Location
The “Location” field allows you to specify the city or region where the bank is situated. This helps further clarify the bank’s physical location, especially in the case of branches or subsidiaries in different cities or countries.BIC/SWIFT
The “BIC/SWIFT” field is where you enter the Bank Identifier Code (BIC) or SWIFT code associated with the bank. This code is used for identifying banks during international money transfers. It’s essential for ensuring that payments are accurately routed to the correct institution, particularly for cross-border transactions.
